-
×
 Pairs Trading The Final Frontier with Don Kaufman
1 × $6.00
Pairs Trading The Final Frontier with Don Kaufman
1 × $6.00 -
×
 The Complete Guide to Multiple Time Frame Analysis & Reading Price Action with Aiman Almansoori
1 × $13.00
The Complete Guide to Multiple Time Frame Analysis & Reading Price Action with Aiman Almansoori
1 × $13.00 -
×
 4D Bootcamp with Black Rabbit
1 × $10.00
4D Bootcamp with Black Rabbit
1 × $10.00 -
×
 Power Cycle Trading The Ultimate Option Guide: When & How to Use Which Option Strategy For the Best Results - Powercycletrading
1 × $69.00
Power Cycle Trading The Ultimate Option Guide: When & How to Use Which Option Strategy For the Best Results - Powercycletrading
1 × $69.00 -
×
 Carolyn Boroden Package
1 × $15.00
Carolyn Boroden Package
1 × $15.00 -
×
 How To Flip All Those “Hard To Flip” Deals
1 × $6.00
How To Flip All Those “Hard To Flip” Deals
1 × $6.00 -
×
 All About Market Timing with Leslie N.Masonson
1 × $6.00
All About Market Timing with Leslie N.Masonson
1 × $6.00 -
×
 An Introduction to Option Trading Success with James Bittman
1 × $6.00
An Introduction to Option Trading Success with James Bittman
1 × $6.00 -
×
 The Orderflow Masterclass with PrimeTrading
1 × $17.00
The Orderflow Masterclass with PrimeTrading
1 × $17.00 -
×
 Options Trading & Ultimate MasterClass With Tyrone Abela - FX Evolution
1 × $54.00
Options Trading & Ultimate MasterClass With Tyrone Abela - FX Evolution
1 × $54.00 -
×
 Fast Track Course with Tradelikerocket
1 × $233.00
Fast Track Course with Tradelikerocket
1 × $233.00 -
×
 LARGE CAP MOMENTUM STRATEGY with Nick Radge
1 × $179.00
LARGE CAP MOMENTUM STRATEGY with Nick Radge
1 × $179.00 -
×
 ICT Prodigy Trading Course – $650K in Payouts with Alex Solignani
1 × $15.00
ICT Prodigy Trading Course – $650K in Payouts with Alex Solignani
1 × $15.00 -
×
 Butterfly and Condor Workshop with Aeromir
1 × $15.00
Butterfly and Condor Workshop with Aeromir
1 × $15.00 -
×
 Matrix Spread Options Trading Course with Base Camp Trading
1 × $31.00
Matrix Spread Options Trading Course with Base Camp Trading
1 × $31.00 -
×
 All Candlestick Patterns Tested And Ranked with Quantified Strategies
1 × $8.00
All Candlestick Patterns Tested And Ranked with Quantified Strategies
1 × $8.00 -
×
 Self-Mastery Course with Steven Cruz
1 × $62.00
Self-Mastery Course with Steven Cruz
1 × $62.00 -
×
 Options Bootcamp with Sid Woolfolk
1 × $6.00
Options Bootcamp with Sid Woolfolk
1 × $6.00 -
×
 George Bayer Squarring the Circle for Excel
1 × $6.00
George Bayer Squarring the Circle for Excel
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Professional Trader Course
1 × $5.00
Professional Trader Course
1 × $5.00 -
×
 $20 – 52k 20 pips a day challange with Rafał Zuchowicz - TopMasterTrader
1 × $5.00
$20 – 52k 20 pips a day challange with Rafał Zuchowicz - TopMasterTrader
1 × $5.00 -
×
 Options 201: Vertical and Calendar Spread Essentials 5 Part Class with Don Kaufman On Demand Replay
1 × $6.00
Options 201: Vertical and Calendar Spread Essentials 5 Part Class with Don Kaufman On Demand Replay
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Profiletraders - MARKET PROFILE TACTICAL STRATEGIES FOR DAY TRADING
1 × $23.00
Profiletraders - MARKET PROFILE TACTICAL STRATEGIES FOR DAY TRADING
1 × $23.00 -
×
 Sixpart Study Guide to Market Profile
1 × $6.00
Sixpart Study Guide to Market Profile
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Fast Start Barter System with Bob Meyer
1 × $31.00
Fast Start Barter System with Bob Meyer
1 × $31.00 -
×
 Best of AM Review (Volume 1-3) with Peter Bain
1 × $6.00
Best of AM Review (Volume 1-3) with Peter Bain
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Trading 3SMA System with Hector DeVille
1 × $6.00
Trading 3SMA System with Hector DeVille
1 × $6.00 -
×
 The Adventures of the Cycle Hunter. The Analyst with Craig Bttlc
1 × $6.00
The Adventures of the Cycle Hunter. The Analyst with Craig Bttlc
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Candlestick Secrets For Profiting In Options
1 × $23.00
Candlestick Secrets For Profiting In Options
1 × $23.00 -
×
 Naked Forex: High-Probability Techniques for Trading Without Indicators (2012) with Alex Nekritin & Walter Peters
1 × $6.00
Naked Forex: High-Probability Techniques for Trading Without Indicators (2012) with Alex Nekritin & Walter Peters
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Ultimate Trading Course with Dodgy's Dungeon
1 × $8.00
Ultimate Trading Course with Dodgy's Dungeon
1 × $8.00 -
×
 7 Days Options Masters Course with John Carter
1 × $54.00
7 Days Options Masters Course with John Carter
1 × $54.00 -
×
 Algo Trading Masterclass with Ali Casey - StatOasis
1 × $23.00
Algo Trading Masterclass with Ali Casey - StatOasis
1 × $23.00 -
×
 Investment Leadership & Portfolio Management with Brian Singer
1 × $6.00
Investment Leadership & Portfolio Management with Brian Singer
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Psycho-Paper 96 with Charles Drummond
1 × $6.00
Psycho-Paper 96 with Charles Drummond
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Day One Trader with John Sussex
1 × $6.00
Day One Trader with John Sussex
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Trading Masterclass XVII with Wysetrade
1 × $6.00
Trading Masterclass XVII with Wysetrade
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Fundamentals of the Securities Industry with William A.Rini
1 × $6.00
Fundamentals of the Securities Industry with William A.Rini
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Essentials in Quantitative Trading QT01 By HangukQuant's
1 × $23.00
Essentials in Quantitative Trading QT01 By HangukQuant's
1 × $23.00 -
×
 How the Stock Market Works with Ramon DeGennaro
1 × $5.00
How the Stock Market Works with Ramon DeGennaro
1 × $5.00 -
×
 8 Year Presidential Election Pattern (Article) with Adam White
1 × $6.00
8 Year Presidential Election Pattern (Article) with Adam White
1 × $6.00 -
×
 The Naked Eye: Raw Data Analytics with Edgar Torres - Raw Data Analytics
1 × $8.00
The Naked Eye: Raw Data Analytics with Edgar Torres - Raw Data Analytics
1 × $8.00 -
×
 Original Curriculum with Home Options Trading Course
1 × $6.00
Original Curriculum with Home Options Trading Course
1 × $6.00 -
×
 The 80% Solution S&P Systems with Bruce Babcock
1 × $6.00
The 80% Solution S&P Systems with Bruce Babcock
1 × $6.00 -
×
 A Grand Supercycle Top Webinar with Steven Hochberg
1 × $6.00
A Grand Supercycle Top Webinar with Steven Hochberg
1 × $6.00 -
×
 How To Become StressFree Trader with Jason Starzec
1 × $4.00
How To Become StressFree Trader with Jason Starzec
1 × $4.00 -
×
 Generative AI for Asset Managers Workshop Recording with Ernest Chan
1 × $55.00
Generative AI for Asset Managers Workshop Recording with Ernest Chan
1 × $55.00 -
×
 Core Strategy Program + Extended Learning Track with Ota Courses
1 × $124.00
Core Strategy Program + Extended Learning Track with Ota Courses
1 × $124.00 -
×
 Pattern Recognition: A Fundamental Introduction to Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques Class with Jeff Bierman
1 × $6.00
Pattern Recognition: A Fundamental Introduction to Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques Class with Jeff Bierman
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Equity Valuation for Analysts and Investors: A Unique Stock Valuation Tool for Financial Statement Analysis and Model-Building with James Kelleher
1 × $6.00
Equity Valuation for Analysts and Investors: A Unique Stock Valuation Tool for Financial Statement Analysis and Model-Building with James Kelleher
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Candlestick - Training Videos (Videos 1.2 GB)
1 × $15.00
Candlestick - Training Videos (Videos 1.2 GB)
1 × $15.00 -
×
 8 Strategies for Day Trading
1 × $31.00
8 Strategies for Day Trading
1 × $31.00 -
×
 3 Volatility Strategies with Quantified Strategies
1 × $23.00
3 Volatility Strategies with Quantified Strategies
1 × $23.00 -
×
 Secret Income with James Altucher
1 × $62.00
Secret Income with James Altucher
1 × $62.00
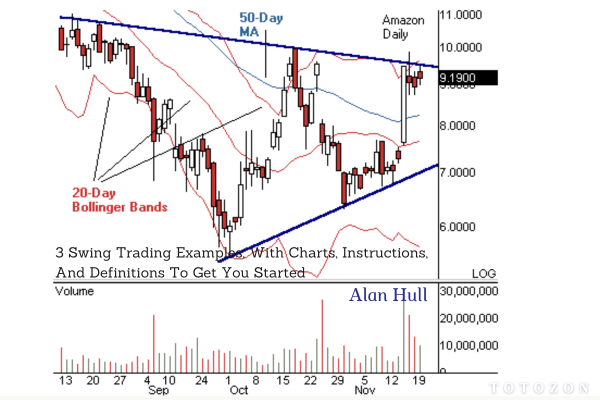
3 Swing Trading Examples, With Charts, Instructions, And Definitions To Get You Started by Alan Farley
$6.00
File Size: Cooming soon!
Delivery Time: 1–12 hours
Media Type: Online Course
Content Proof: Watch Here!
You may check content proof of “3 Swing Trading Examples, With Charts, Instructions, And Definitions To Get You Started by Alan Farley” below:
3 Swing Trading Examples, With Charts, Instructions, And Definitions To Get You Started by Alan Farley
Introduction
Swing trading is a popular strategy for capturing short- to medium-term gains in the stock market. Alan Farley, a seasoned trading expert, provides insightful examples that can help beginners and experienced traders alike. This article will walk you through three swing trading examples with charts, detailed instructions, and key definitions to get you started on your trading journey.
What is Swing Trading?
Definition
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks, aiming to profit from price swings. This strategy capitalizes on short-term trends and market volatility.
Why Choose Swing Trading?
Swing trading offers flexibility and requires less time commitment compared to day trading, making it suitable for individuals with other commitments.
Key Terms in Swing Trading
1. Entry Point
The price at which a trader buys a stock, initiating the trade.
2. Exit Point
The price at which a trader sells a stock, concluding the trade.
3. Stop-Loss Order
An order placed to sell a stock when it reaches a certain price, limiting potential losses.
4. Resistance Level
A price level at which a stock tends to stop rising, encountering selling pressure.
5. Support Level
A price level at which a stock tends to stop falling, encountering buying interest.
Swing Trading Example 1: Moving Average Crossover
Step-by-Step Instructions
1. Identify the Moving Averages
Use a 50-day simple moving average (SMA) and a 200-day SMA. These averages help identify the overall trend.
2. Look for a Crossover
A bullish signal occurs when the 50-day SMA crosses above the 200-day SMA, indicating a potential uptrend.
3. Enter the Trade
Buy the stock when the crossover is confirmed.
4. Set a Stop-Loss Order
Place a stop-loss order below a recent support level to manage risk.
5. Determine the Exit Point
Sell the stock when the 50-day SMA crosses below the 200-day SMA, indicating a potential downtrend.
Chart Example
Swing Trading Example 2: RSI Overbought/Oversold
Step-by-Step Instructions
1. Set Up the RSI Indicator
Use the Relative Strength Index (RSI) with a 14-day period. RSI measures the speed and change of price movements.
2. Identify Overbought/Oversold Conditions
RSI values above 70 indicate overbought conditions, while values below 30 indicate oversold conditions.
3. Enter the Trade
- Buy Signal: When RSI moves below 30 and then rises back above it, indicating the stock is recovering from oversold conditions.
- Sell Signal: When RSI moves above 70 and then falls back below it, indicating the stock is retreating from overbought conditions.
4. Set a Stop-Loss Order
Place a stop-loss order below the recent low for a buy signal or above the recent high for a sell signal.
5. Determine the Exit Point
Exit the trade when RSI returns to neutral levels (typically around 50) or if a stop-loss is triggered.
Chart Example
Swing Trading Example 3: Cup and Handle Pattern
Step-by-Step Instructions
1. Identify the Pattern
Look for a “cup” shape on the price chart, followed by a small consolidation forming the “handle.”
2. Confirm the Pattern
The cup should be U-shaped and not too deep, with the handle forming near the cup’s high point.
3. Enter the Trade
Buy the stock when the price breaks out above the handle’s resistance level.
4. Set a Stop-Loss Order
Place a stop-loss order below the bottom of the handle to manage risk.
5. Determine the Exit Point
Sell the stock at a predetermined profit target, often calculated as the height of the cup added to the breakout point.
Chart Example
Conclusion
Swing trading can be a highly effective strategy for capturing gains in the stock market. By following Alan Farley’s examples and using the right technical tools, you can enhance your trading skills and increase your chances of success. Remember, consistency and risk management are key to profitable trading.
FAQs
1. What is the best time frame for swing trading?
Swing trading typically involves holding positions for several days to weeks, so daily and weekly charts are most useful.
2. How much capital do I need to start swing trading?
The amount of capital needed can vary, but starting with at least $5,000 to $10,000 is recommended to allow for diversification and risk management.
3. Can swing trading be automated?
Yes, many traders use automated trading systems and algorithms to execute swing trades based on predefined criteria.
4. How do I choose the right stocks for swing trading?
Look for stocks with high liquidity, clear trends, and significant price swings. Screen for technical indicators that align with your strategy.
5. Is swing trading suitable for beginners?
Swing trading can be suitable for beginners, especially those who take the time to learn and practice basic trading principles and risk management.
Be the first to review “3 Swing Trading Examples, With Charts, Instructions, And Definitions To Get You Started by Alan Farley” Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a review.
Related products
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
The Complete Guide to Multiple Time Frame Analysis & Reading Price Action with Aiman Almansoori
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading


















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.