-
×
 The Great Depression with David Burg
1 × $6.00
The Great Depression with David Burg
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Options Trading & Ultimate MasterClass With Tyrone Abela - FX Evolution
1 × $54.00
Options Trading & Ultimate MasterClass With Tyrone Abela - FX Evolution
1 × $54.00 -
×
 Forecast 2024 Clarification with Larry Williams
1 × $15.00
Forecast 2024 Clarification with Larry Williams
1 × $15.00 -
×
 Setups of a Winning Trader with Gareth Soloway
1 × $521.00
Setups of a Winning Trader with Gareth Soloway
1 × $521.00 -
×
 P.A.T Trading Course (Low Video Quality) with Martin Cole
1 × $6.00
P.A.T Trading Course (Low Video Quality) with Martin Cole
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Path to Profits By Scott Redler - T3 Live
1 × $6.00
Path to Profits By Scott Redler - T3 Live
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Home Run Options Trading Course with Dave Aquino - Base Camp Trading
1 × $11.00
Home Run Options Trading Course with Dave Aquino - Base Camp Trading
1 × $11.00 -
×
 Consistently Profitable Trader with Pollinate Trading
1 × $13.00
Consistently Profitable Trader with Pollinate Trading
1 × $13.00 -
×
 Road to consistent profits (Dec 2022) with Jarrod Goodwin - Trading Halls of Knowledge
1 × $31.00
Road to consistent profits (Dec 2022) with Jarrod Goodwin - Trading Halls of Knowledge
1 × $31.00 -
×
 The Stock Rocket Trading System with Dave Wooding
1 × $6.00
The Stock Rocket Trading System with Dave Wooding
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Acclimation Course with Base Camp Trading
1 × $10.00
Acclimation Course with Base Camp Trading
1 × $10.00 -
×
 Asset Prices, Booms & Recessions (2nd Ed.) with Willi Semmler
1 × $6.00
Asset Prices, Booms & Recessions (2nd Ed.) with Willi Semmler
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Quantamentals - The Next Great Forefront Of Trading and Investing with Trading Markets
1 × $8.00
Quantamentals - The Next Great Forefront Of Trading and Investing with Trading Markets
1 × $8.00 -
×
 How to Buy Stocks Before They Skyrocket
1 × $6.00
How to Buy Stocks Before They Skyrocket
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Tomorrow's Gold: Asia's Age of Discovery with Marc Faber
1 × $6.00
Tomorrow's Gold: Asia's Age of Discovery with Marc Faber
1 × $6.00 -
×
 How I use Technical Analysis & Orderflow with Adam Webb - Traderskew
1 × $54.00
How I use Technical Analysis & Orderflow with Adam Webb - Traderskew
1 × $54.00 -
×
 The Any Hour Trading System with Markets Mastered
1 × $6.00
The Any Hour Trading System with Markets Mastered
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Order flow self-study training program with iMFtracker
1 × $10.00
Order flow self-study training program with iMFtracker
1 × $10.00 -
×
 TRADING NFX Course with Andrew NFX
1 × $5.00
TRADING NFX Course with Andrew NFX
1 × $5.00 -
×
 Deep Dive Butterfly Trading Strategy Class with SJG Trades
1 × $41.00
Deep Dive Butterfly Trading Strategy Class with SJG Trades
1 × $41.00 -
×
 Trading Short TermSame Day Trades Sep 2023 with Dan Sheridan & Mark Fenton - Sheridan Options Mentoring
1 × $31.00
Trading Short TermSame Day Trades Sep 2023 with Dan Sheridan & Mark Fenton - Sheridan Options Mentoring
1 × $31.00 -
×
 T3 Live - The Simple Art of Trading
1 × $31.00
T3 Live - The Simple Art of Trading
1 × $31.00 -
×
 Secrets of An Electronic Futures Trader with Larry Levin
1 × $6.00
Secrets of An Electronic Futures Trader with Larry Levin
1 × $6.00 -
×
 The Trading Blueprint with Brad Goh - The Trading Geek
1 × $5.00
The Trading Blueprint with Brad Goh - The Trading Geek
1 × $5.00 -
×
 Advanced Trading System - How To 10x Your Trading Skillsets & Results with The Trade Academy
1 × $6.00
Advanced Trading System - How To 10x Your Trading Skillsets & Results with The Trade Academy
1 × $6.00 -
×
 5-Week Portfolio (No Bonus) - Criticaltrading
1 × $39.00
5-Week Portfolio (No Bonus) - Criticaltrading
1 × $39.00 -
×
 Bond Market Course with The Macro Compass
1 × $15.00
Bond Market Course with The Macro Compass
1 × $15.00 -
×
 Financial Freedom Mastery Course with Freedom Team Trading
1 × $31.00
Financial Freedom Mastery Course with Freedom Team Trading
1 × $31.00 -
×
 How To Read The Market Professionally with TradeSmart
1 × $27.00
How To Read The Market Professionally with TradeSmart
1 × $27.00 -
×
 Gold Trading Boot Camp: How to Master the Basics and Become a Successful Commodities Investor - Gregory Weldon & Dennis Gartman
1 × $6.00
Gold Trading Boot Camp: How to Master the Basics and Become a Successful Commodities Investor - Gregory Weldon & Dennis Gartman
1 × $6.00 -
×
 A+ Setups Big Caps Options with Jtrader
1 × $6.00
A+ Setups Big Caps Options with Jtrader
1 × $6.00 -
×
 The Best Option Trading Course with David Jaffee - Best Stock Strategy
1 × $15.00
The Best Option Trading Course with David Jaffee - Best Stock Strategy
1 × $15.00 -
×
 0 DTE Options Trading Workshop with Aeromir Corporation
1 × $15.00
0 DTE Options Trading Workshop with Aeromir Corporation
1 × $15.00 -
×
 Compass Trading System with Right Line Trading
1 × $39.00
Compass Trading System with Right Line Trading
1 × $39.00 -
×
 ICT Prodigy Trading Course – $650K in Payouts with Alex Solignani
1 × $15.00
ICT Prodigy Trading Course – $650K in Payouts with Alex Solignani
1 × $15.00 -
×
 The Practical Handbook of Genetic Algorithms with Lance Chambers
1 × $6.00
The Practical Handbook of Genetic Algorithms with Lance Chambers
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Recover Your Losses & Double Your Account Size with Tokyo The Trader - PLFCrypto
1 × $6.00
Recover Your Losses & Double Your Account Size with Tokyo The Trader - PLFCrypto
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Scalp Strategy and Flipping Small Accounts with Opes Trading Group
1 × $5.00
Scalp Strategy and Flipping Small Accounts with Opes Trading Group
1 × $5.00 -
×
 Options 201: Vertical and Calendar Spread Essentials 5 Part Class with Don Kaufman On Demand Replay
1 × $6.00
Options 201: Vertical and Calendar Spread Essentials 5 Part Class with Don Kaufman On Demand Replay
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Private Mentorship with ANICO Capital
1 × $10.00
Private Mentorship with ANICO Capital
1 × $10.00 -
×
 A Momentum Based Approach to Swing Trading with Dave Landry
1 × $6.00
A Momentum Based Approach to Swing Trading with Dave Landry
1 × $6.00 -
×
 The Logical Trader: Applying a Method to the Madness with Mark Fisher
1 × $6.00
The Logical Trader: Applying a Method to the Madness with Mark Fisher
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Core Strategy Program + Extended Learning Track with Ota Courses
1 × $124.00
Core Strategy Program + Extended Learning Track with Ota Courses
1 × $124.00 -
×
 FlowRider Trading Course with Boris Schlossberg and Kathy Lien - Bkforex
1 × $15.00
FlowRider Trading Course with Boris Schlossberg and Kathy Lien - Bkforex
1 × $15.00 -
×
 5-Step-Trading Stocks I and II with Lex Van Dam
1 × $4.00
5-Step-Trading Stocks I and II with Lex Van Dam
1 × $4.00 -
×
 Trading by the Book (tradingeducators.com)
1 × $6.00
Trading by the Book (tradingeducators.com)
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Simple Methods for Detecting Buying and Selling Points in Securities with James Liveright
1 × $6.00
Simple Methods for Detecting Buying and Selling Points in Securities with James Liveright
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Day One Trader with John Sussex
1 × $6.00
Day One Trader with John Sussex
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Pristine - Cardinal Rules of Trading
1 × $6.00
Pristine - Cardinal Rules of Trading
1 × $6.00 -
×
 8 Strategies for Day Trading
1 × $31.00
8 Strategies for Day Trading
1 × $31.00 -
×
 BigTrends Home Study Course
1 × $6.00
BigTrends Home Study Course
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Crystal Ball Pack PLUS bonus Live Trade By Pat Mitchell - Trick Trades
1 × $20.00
Crystal Ball Pack PLUS bonus Live Trade By Pat Mitchell - Trick Trades
1 × $20.00 -
×
 How to Trade Diagonal Triangles. Superior Risk Reward Trade Setups
1 × $6.00
How to Trade Diagonal Triangles. Superior Risk Reward Trade Setups
1 × $6.00 -
×
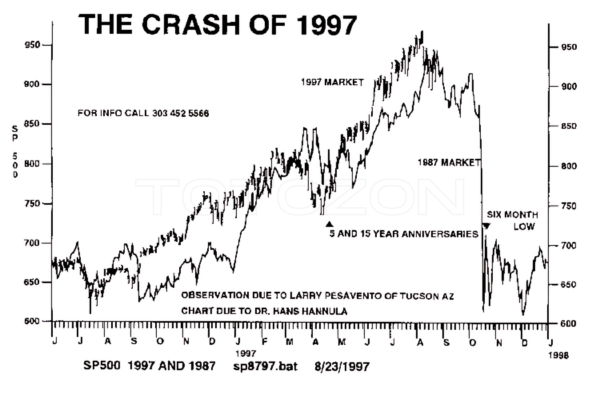 The Crash of 1997 (Article) with Hans Hannula
1 × $6.00
The Crash of 1997 (Article) with Hans Hannula
1 × $6.00 -
×
 DiNapoli Levels Training Course with Joe DiNapoli & Merrick Okamoto
1 × $6.00
DiNapoli Levels Training Course with Joe DiNapoli & Merrick Okamoto
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Advanced Bond Trading Course
1 × $62.00
Advanced Bond Trading Course
1 × $62.00 -
×
 5 Technical Signals You Should Not Trade Without (4 CDs) with Toni Hansen
1 × $6.00
5 Technical Signals You Should Not Trade Without (4 CDs) with Toni Hansen
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Advanced Iron Condor Course in 2021
1 × $6.00
Advanced Iron Condor Course in 2021
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Short-Term Trading with Precision Timing - Jack Bernstein
1 × $6.00
Short-Term Trading with Precision Timing - Jack Bernstein
1 × $6.00 -
×
 High Probability Trading Using Elliott Wave And Fibonacci Analysis withVic Patel - Forex Training Group
1 × $10.00
High Probability Trading Using Elliott Wave And Fibonacci Analysis withVic Patel - Forex Training Group
1 × $10.00 -
×
 Practical Approach to Trend Following By Rajandran R
1 × $15.00
Practical Approach to Trend Following By Rajandran R
1 × $15.00 -
×
 RSI Unleashed: Building a Comprehensive Trading Framework By Doc Severson
1 × $6.00
RSI Unleashed: Building a Comprehensive Trading Framework By Doc Severson
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Commodities and Commodity Derivatives: Modeling and Pricing for Agriculturals, Metals and Energy - Helyette Geman
1 × $6.00
Commodities and Commodity Derivatives: Modeling and Pricing for Agriculturals, Metals and Energy - Helyette Geman
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Fixed-Income Securities: Valuation, Risk Management and Portfolio Strategies - Lionel Martellini, Philippe Priaulet & Stéphane Priaulet
1 × $6.00
Fixed-Income Securities: Valuation, Risk Management and Portfolio Strategies - Lionel Martellini, Philippe Priaulet & Stéphane Priaulet
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Essentials in Quantitative Trading QT01 By HangukQuant's
1 × $23.00
Essentials in Quantitative Trading QT01 By HangukQuant's
1 × $23.00 -
×
 Synthetic and Structured Assets: A Practical Guide to Investment and Risk with Erik Banks
1 × $6.00
Synthetic and Structured Assets: A Practical Guide to Investment and Risk with Erik Banks
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Butterfly and Condor Workshop with Aeromir
1 × $15.00
Butterfly and Condor Workshop with Aeromir
1 × $15.00 -
×
 Fixed Income Securities (2nd Ed.) with Bruce Tuckman
1 × $10.00
Fixed Income Securities (2nd Ed.) with Bruce Tuckman
1 × $10.00 -
×
 Volume Profile 2023 (Elite Pack) with Trader Dale
1 × $5.00
Volume Profile 2023 (Elite Pack) with Trader Dale
1 × $5.00 -
×
 Matrix Spread Options Trading Course with Base Camp Trading
1 × $31.00
Matrix Spread Options Trading Course with Base Camp Trading
1 × $31.00 -
×
 Handbook of Integral Equations with Andrei D.Polyanin, Alexander V.Manzhirov
1 × $6.00
Handbook of Integral Equations with Andrei D.Polyanin, Alexander V.Manzhirov
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Profit Before Work System with John Piper
1 × $6.00
Profit Before Work System with John Piper
1 × $6.00 -
×
 NASDAQ Level II Trading Strategies
1 × $6.00
NASDAQ Level II Trading Strategies
1 × $6.00 -
×
 MACD Divergence Fully Automatic Indicator for ThinkOrSwim TOS
1 × $6.00
MACD Divergence Fully Automatic Indicator for ThinkOrSwim TOS
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Advanced Technical Strategies Home Study Course with T3 LIVE
1 × $31.00
Advanced Technical Strategies Home Study Course with T3 LIVE
1 × $31.00 -
×
 Profit Generating System with Brian Williams
1 × $6.00
Profit Generating System with Brian Williams
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Pristine - Trading the Pristine Method 2
1 × $6.00
Pristine - Trading the Pristine Method 2
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Precise Planetary Timing for Stock Trading
1 × $6.00
Precise Planetary Timing for Stock Trading
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Fibonacci for the Active Trader with Derrik Hobbs
1 × $6.00
Fibonacci for the Active Trader with Derrik Hobbs
1 × $6.00 -
×
 A Course in Trading with Donald Mack & Wetsel Market Bureau
1 × $6.00
A Course in Trading with Donald Mack & Wetsel Market Bureau
1 × $6.00 -
×
 Four Dimensional Stock Market Structures & Cycles with Bradley Cowan
1 × $6.00
Four Dimensional Stock Market Structures & Cycles with Bradley Cowan
1 × $6.00
Linear Regression 3030 with David Elliott
$6.00
File Size: Coming soon!
Delivery Time: 1–12 hours
Media Type: Online Course
Content Proof: Watch Here!
You may check content proof of “Linear Regression 3030 with David Elliott” below:
Linear Regression 3030 with David Elliott
Introduction
Linear regression is a powerful statistical tool used for predicting and analyzing relationships between variables. David Elliott’s “Linear Regression 3030” offers a comprehensive guide to mastering this technique. In this article, we explore Elliott’s approach, delving into the key concepts, applications, and benefits of linear regression in various fields.
Understanding Linear Regression
Linear regression is a method used to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
What is Linear Regression?
Linear regression aims to fit a linear equation to observed data. The formula for a simple linear regression is:
Y=β0+β1X+ϵY = \beta_0 + \beta_1X + \epsilonY=β0+β1X+ϵ
where:
- YYY is the dependent variable,
- XXX is the independent variable,
- β0\beta_0β0 is the intercept,
- β1\beta_1β1 is the slope,
- ϵ\epsilonϵ is the error term.
Key Components
- Dependent Variable: The variable we aim to predict or explain.
- Independent Variable: The variable used to make predictions.
- Intercept (β0\beta_0β0): The expected value of YYY when XXX is zero.
- Slope (β1\beta_1β1): The change in YYY for a one-unit change in XXX.
Why Use Linear Regression?
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement.
- Predictive Power: Provides a basis for making predictions.
- Interpretability: Clear interpretation of coefficients.
Types of Linear Regression
Simple Linear Regression
Simple linear regression involves one dependent variable and one independent variable.
Example Application
Predicting a student’s test scores based on the number of study hours.
Multiple Linear Regression
Multiple linear regression involves one dependent variable and multiple independent variables.
Example Application
Predicting house prices based on features like size, location, and age.
Steps to Perform Linear Regression
1. Data Collection
Gather relevant data for analysis.
Key Considerations
- Quality: Ensure data accuracy and completeness.
- Quantity: Adequate sample size for reliable results.
2. Data Preparation
Prepare data for analysis by cleaning and transforming it as necessary.
Data Cleaning
- Remove Outliers: Identify and remove outliers that can skew results.
- Handle Missing Values: Impute or remove missing data points.
3. Model Selection
Choose the appropriate linear regression model (simple or multiple).
Model Considerations
- Number of Variables: Determine if you need a simple or multiple regression model.
- Assumptions: Ensure data meets the assumptions of linear regression.
4. Model Fitting
Fit the linear regression model to the data using statistical software.
Software Options
- Excel: Basic linear regression analysis.
- R: Advanced statistical analysis.
- Python: Versatile programming for data analysis.
5. Model Evaluation
Evaluate the model’s performance using various metrics.
Evaluation Metrics
- R-squared: Proportion of variance in the dependent variable explained by the model.
- Adjusted R-squared: Adjusted for the number of predictors in the model.
- Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): Measures the average error of the model’s predictions.
Interpreting Linear Regression Results
Coefficients
The coefficients indicate the relationship between each independent variable and the dependent variable.
Interpreting Coefficients
- Positive Coefficient: Indicates a positive relationship.
- Negative Coefficient: Indicates a negative relationship.
Statistical Significance
Assess the significance of the model and its coefficients using p-values.
P-Value Interpretation
- Low P-Value (< 0.05): Indicates statistical significance.
- High P-Value (> 0.05): Indicates lack of statistical significance.
Applications of Linear Regression
Finance
Linear regression is widely used in finance for risk management, portfolio optimization, and predicting stock prices.
Example
Using linear regression to predict future stock prices based on historical data.
Healthcare
In healthcare, linear regression can predict patient outcomes and identify risk factors.
Example
Predicting patient recovery times based on age, medical history, and treatment type.
Marketing
Marketers use linear regression to understand the impact of different factors on sales and customer behavior.
Example
Analyzing the effect of advertising spend on sales revenue.
Benefits of Linear Regression
Predictive Accuracy
Provides accurate predictions when assumptions are met.
Key Benefits
- Forecasting: Helps in making future predictions.
- Decision Making: Informs strategic business decisions.
Simplicity and Interpretability
Easy to understand and interpret results.
User-Friendly
- Clear Results: Straightforward interpretation of coefficients.
- Wide Application: Applicable across various fields.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Assumption Violations
Linear regression relies on several assumptions that must be met for accurate results.
Key Assumptions
- Linearity: The relationship between the variables is linear.
- Independence: Observations are independent of each other.
- Homoscedasticity: Constant variance of errors.
- Normality: The errors are normally distributed.
Overfitting
Including too many variables can lead to overfitting.
Avoiding Overfitting
- Cross-Validation: Use cross-validation techniques to test the model.
- Simplify Model: Include only significant predictors.
Advanced Techniques in Linear Regression
Regularization
Regularization techniques like Lasso and Ridge regression help prevent overfitting.
Lasso Regression
Penalizes the absolute size of the coefficients.
Ridge Regression
Penalizes the square of the coefficients.
Polynomial Regression
Extends linear regression by fitting a polynomial equation to the data.
When to Use
Use polynomial regression when the relationship between variables is nonlinear.
Conclusion
David Elliott’s “Linear Regression 3030” offers a detailed guide to understanding and applying linear regression in various fields. By mastering the steps and techniques outlined, you can leverage linear regression to make accurate predictions and informed decisions, enhancing your analytical capabilities and achieving better outcomes.

FAQs
1. What is linear regression used for?
Linear regression is used to model and predict the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
2. How do you interpret the coefficients in a linear regression model?
Coefficients represent the change in the dependent variable for a one-unit change in the independent variable, holding all other variables constant.
3. What are the key assumptions of linear regression?
Key assumptions include linearity, independence, homoscedasticity, and normality of errors.
4. How can you avoid overfitting in linear regression?
Avoid overfitting by using cross-validation techniques and simplifying the model by including only significant predictors.
5. What is the difference between simple and multiple linear regression?
Simple linear regression involves one dependent and one independent variable, while multiple linear regression involves one dependent variable and multiple independent variables.
Be the first to review “Linear Regression 3030 with David Elliott” Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a review.
Related products
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading
Forex Trading











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.